Voronoi
The voronoi type defines a prior model defines an a priori model based on a number of Voronoi cells. For example, a 2D model of size (20x20) with 50 randomly located Voronoi cells can be defined using
cells_N_max=50;
ip=1;
prior{ip}.type='voronoi';
prior{ip}.x=1:.04:20;
prior{ip}.y=1:.04:20;
prior{ip}.cells_N=cells_N_max; % SET NUMBER OF CELLS
prior{ip}.cells_N_min=3;
prior{ip}.cells_N_max=cells_N_max;
sippi_plot_prior_sample(prior);
The value of each cell is simply an integer number between 1 and prior{ip}.cells_N.
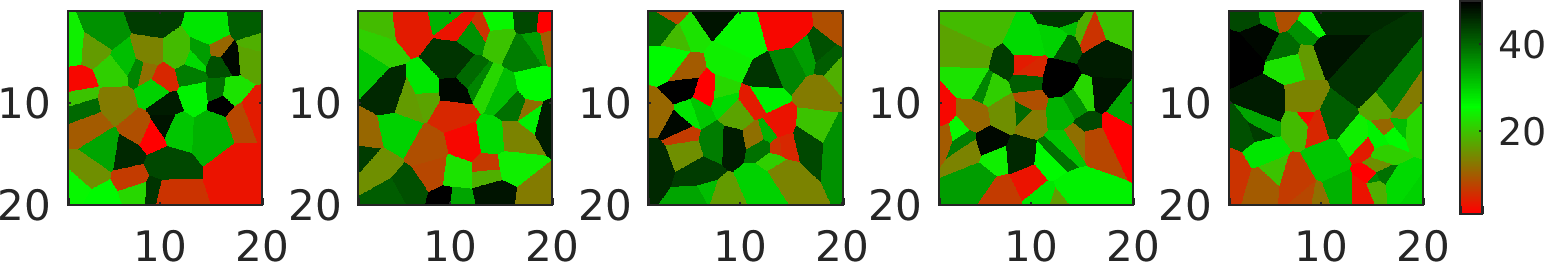
Randomize number of, location of, and value of the Voronois cells
The location and value of the Voronois cells can be randomized by specifying additional, appropriately named a priori types.
For example to randomize location of the Voronoi cell define a number prior models with names cells_x, cells_y, and cells_z (in 3D), as e.g.:
ip=ip+1;
prior{ip}.type='uniform';
prior{ip}.name='cells_x';
prior{ip}.x=[1:cells_N_max];
prior{ip}.min=min(prior{1}.x);
prior{ip}.max=max(prior{1}.x);
prior{ip}.cax=[prior{ip}.min prior{ip}.max];
prior{ip}.prior_master=1;
ip=ip+1;
prior{ip}.type='uniform';
prior{ip}.name='cells_y';
prior{ip}.x=[1:cells_N_max];
prior{ip}.min=min(prior{1}.y);
prior{ip}.max=max(prior{1}.y);
prior{ip}.cax=[prior{ip}.min prior{ip}.max];
prior{ip}.prior_master=1;
Finally, to randomize the value of each cell, define a prior with name cells_value, as e.g.
ip=ip+1;
prior{ip}.type='uniform';
prior{ip}.name='cells_value';
prior{ip}.x=[1:cells_N_max];
prior{ip}.min=5;
prior{ip}.max=15;
prior{ip}.prior_master=1;
prior{1}.cax=[5 15];
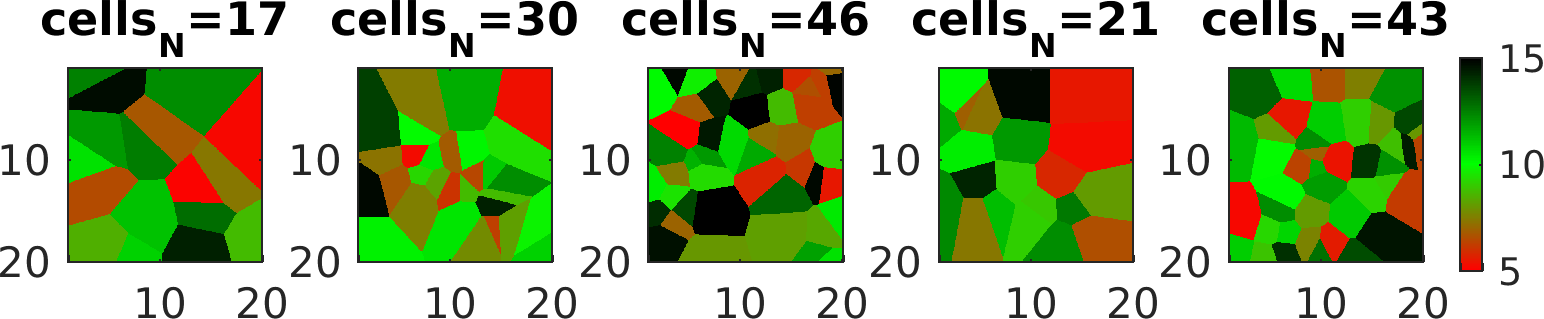
Random walk using sequential Gibbs sampling
A random walk in the uniform prior (as in any supported prior type) can be obtained using sequential Gibbs sampling:
for i=1:500;
[m,prior]=sippi_prior(prior,m);
sippi_plot_prior(prior,m);
drawnow;
end
This provides a video as e.g.:
The code for the full example can be found here: prior_reals_voronoi.m.